Laparoscopic
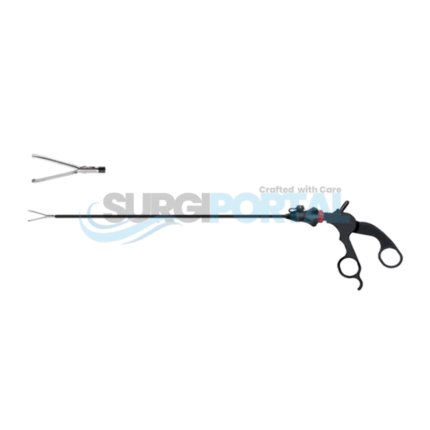
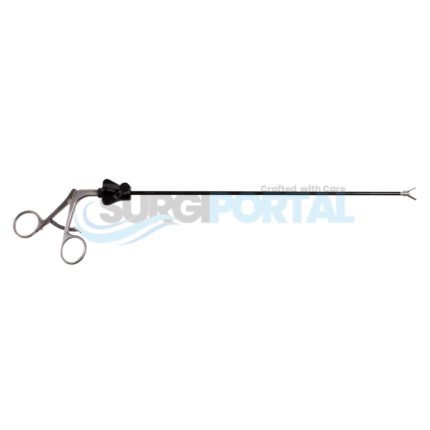
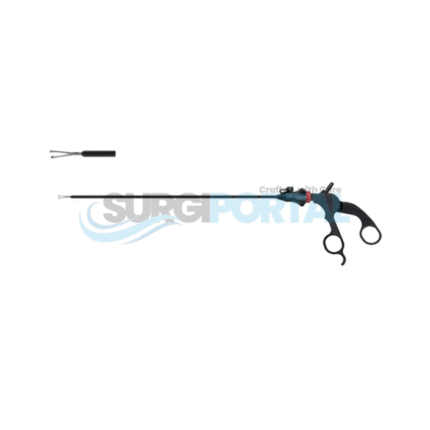
Laparoscopic instruments are precision-engineered surgical tools designed for performing minimally invasive procedures through small abdominal incisions. Used extensively in general surgery, gynecology, urology, bariatric, and gastrointestinal operations, these instruments allow surgeons to operate with exceptional accuracy, reduced tissue trauma, and faster patient recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
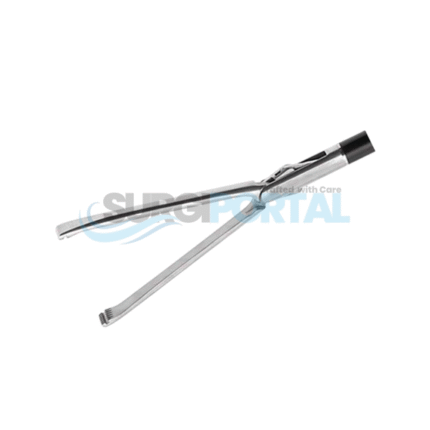
Crafted from high-grade medical stainless steel and advanced polymer materials, laparoscopic instruments maintain durability, sterility, and performance even in demanding surgical environments. Common designs include graspers, dissectors, scissors, clip applicators, suction–irrigation devices, trocars, and electrosurgical instruments such as hook electrodes and spatula probes. Each tool is engineered to provide precise control inside the confined space of the abdominal cavity, often with insulated shafts to ensure safe energy delivery during monopolar or bipolar electrosurgery.
Typical applications include laparoscopic cholecystectomy, appendectomy, hernia repair, adhesiolysis, colorectal surgery, endometriosis excision, gastric bypass, and sleeve gastrectomy. The slender, elongated shafts (generally 33–45 cm in length) and ergonomic handles allow surgeons to access deep or delicate anatomical areas through standard 5 mm or 10 mm trocars while maintaining clear visualization through a laparoscope.
Available in both reusable and single-use variants, laparoscopic instruments are designed to support strict sterilization protocols and infection control measures. Reusable models can withstand repeated autoclave cycles without compromising mechanical integrity or cutting performance, while single-use models provide maximum convenience and eliminate the risk of cross-contamination.
With their combination of safety, precision, and adaptability, laparoscopic instruments remain essential to modern surgical practice, enabling minimally invasive approaches that improve patient comfort, reduce hospital stays, and optimize operative outcomes.